New energy management strategies found for smart microgrids
Jul 07, 2020
With the increased uptake of renewable energy in urban communities, there has been considerably more discussion around the topic of microgrids. Small groups would operate an electrical grid for their community at a lower cost than major retailers, based on the use of renewable energy. Research conducted at Southern University of Science and Technology (SUSTech) has determined some unique energy management strategies that could be applied for smart microgrids across the globe.
Assistant Professor Youwei Jia (Electrical and Electronic Engineering) has led his research group to publish their research results on smart microgrid operations in the high-impact academic journal, IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid (IF = 10.486). Their articles were titled “A Novel Retrospect-inspired Regime for Microgrid Real-time Energy Scheduling with Heterogeneous Sources” and “A Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning based Data-driven Method for Home Energy Management.” A third paper received the Best Paper Award at the virtual 2020 IEEE Power & Energy Society (PES) General Meeting. That paper was titled, “Real-Time Operation Optimization of Islanded Microgrid with Battery Energy Storage System.”
More specifically, smart microgrids represent an emerging paradigm of distributed power systems. It integrates advanced techniques in electricity transmission, monitoring & control, distributed generation, and energy storage. In remote areas, there is an urgent need for improved resilience in power networks, energy security, and electrification. Smart microgrids will continue to play a vital role in global energy transition, but there are significant economic and technological challenges associated with
The first paper published in IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, titled “A Novel Retrospect-inspired Regime for Microgrid Real-time Energy Scheduling with Heterogeneous Sources,” proposed a unique online energy scheduling algorithm to deal with heterogeneous generators in microgrids. The algorithm is unique because it is prediction-oblivious. Hence, it pushes the operation of the microgrid towards economic optimality faster. The paper shows the enormous potential for practical applications in areas including networked microgrids
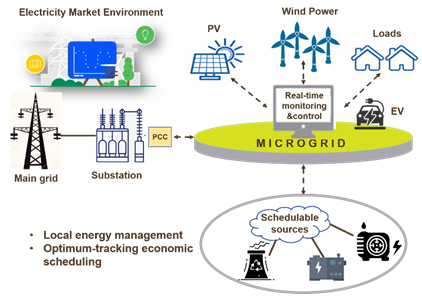
Fig.1 Intelligent microgrid operation
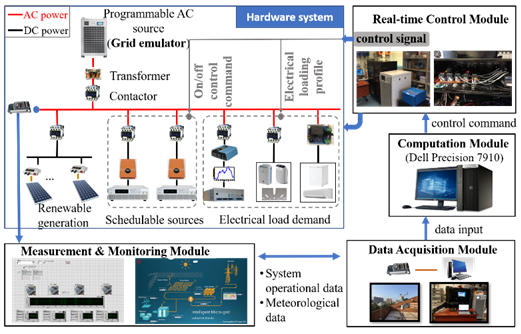
Fig.2 Hardware-in-the-loop Microgrid Platform
SUSTech is the corresponding unit for the paper. Assistant Professor Youwei Jia is the first and corresponding author. Additional contributions came from The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU) and City University of Hong Kong (CityU).
The second paper, titled “A Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning based Data-driven Method for Home Energy Management,” assessed at smart home energy management (HEM) systems. They are commonly used to integrate into smart microgrids to maximize energy efficiency throughout the entire system for all users. HEM systems are now faced with unique challenges with the increased use of rooftop photovoltaic cells for energy generation and the use of electric vehicles. The research team took a data-driven approach to HEM systems to effectively manage different household appliances through the use of smart “agents.” Big data analytics would allow smart homes to assist in the demand-side response to the electricity market. It provides enormous potential for household savings on energy consumption.
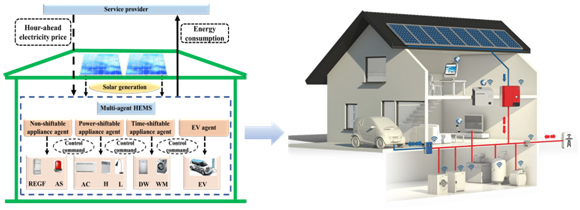
Fig. 3 Smart home energy management
SUSTech is the corresponding unit. Visiting Scholar Dr. Xu Xu is the first author. Assistant Professor Youwei Jia is the correspondent author. Additional contributions came from Nanyang Technological University (NTU), PolyU, and Brunel University London.
The paper published at 2020 IEEE PES that received the Best Paper Award was titled, “Real-Time Operation Optimization of Islanded Microgrid with Battery Energy Storage System.” Energy storage systems (ESS) are essential to provide the flexibility needed for microgrids. As an essential component in the microgrid system, ESS can effectively complement renewable generation and enhance the operational stability. However, quantitatively modeling the cost of the degradation of lithium-ion based ESS becomes a crucial problem in analyzing the economic operation of islanded microgrids.
The paper proposed a real-time energy scheduling approach for islanded microgrid by considering schedulable ESS with detailed degradation cost modeling. Their hypothesis is dedicated to utilizing ESS to achieve power smoothing in renewable energy embedded microgrid operation. It would also avoid battery over-discharge while maximizing energy efficiency and sustainability.
SUSTech is the corresponding unit. Visiting Ph.D. student Mr. Cheng Lyu is the first author. Assistant Professor Youwei Jia is the correspondent author. Additional contributions came from PolyU.
Latest News
Related News